Although video is the dominant mode of global communication, the majority of information is only available in a few languages. As global audiences expand, the demand for multilingual video content has never been greater. Language difficulties continue to be a persistent impediment for everyone, from YouTube producers expanding into Asian markets to multinational corporations educating personnel worldwide.
But artificial intelligence is altering that. The emergence of video and audio translation tools, namely translation systems that combine voice cloning, dubbing, and automatic translation, is changing the way information moves across national boundaries.
This article explains what artificial intelligence (AI) video localization is, how it operates, why 2025 is a significant technical turning point, and the function of technologies like VMEG AI in this new multilingual future.
What Is AI Video Localization and Translation?
Localization and translation are totally different, I have to say. In a nutshell, video translation converts a video’s spoken language (soundtrack) into another, often via subtitles or voiceovers.
Video localization, however, not only translates but can do better; it's adapting tone, emotion, timing, and visuals to fit the target audience’s needs. It can for sure guarantee authenticity, so jokes, emotional scenes, and training content remain effective across languages. In Wikipedia, localization is defined as “translation, cultural adaptation, and technical adjustments to make content suitable for a specific region.”
In old times, localization required a lot of effort, human translators, dubbing artists, and editors — a process that was both time- & money-consuming. AI now automates the key steps:
- Speech recognition (ASR) – transcribes spoken words.
- Machine translation – converts text into the target language.
- Voice synthesis – generates speech in the original speaker’s voice.
The result is a fully translated, dubbed, and culturally adapted video, powered entirely by AI.
Why 2025 Marks a Breakthrough in AI Video Translation
Before 2020, AI translation tools were not unblemished. subtitling is the only thing they can do to help creators leave alone capture tone or speaker identity. However, we've entered a new era. Multimodal AI models, capable of processing audio, text, and video simultaneously, began transforming the field. There are also some Early systems, like Meta’s SeamlessM4T, Google’s Translatotron 2, and OpenAI’s Whisper, that demonstrated near-human speech translation.
In 2025, these technologies have matured, enabling:
- Emotion-preserving voice synthesis that retains tone and expressiveness.
- Cross-lingual voice cloning to “speak” multiple languages without re-recording.
- Context-aware translation for idioms, slang, and regional phrasing.
- Faster rendering, allowing large-scale localization for individual creators.
The consumption of non-English videos on YouTube has increased by more than 75% over the last five years, according to Statista, and this growth has been matched by the unprecedented use of AI translation in marketing, education, and entertainment. The innovation in 2025 goes beyond speed; AI can now express the cultural and emotional content of videos rather than just their words.
How AI Video Localization Works
By and large, the AI video localization pipeline typically includes five technical stages:
- Speech Recognition – AI models like OpenAI Whisper or Deepgram transcribe audio, handling multiple speakers, accents, and background noise, often in multiple languages simultaneously.
- Machine Translation – Neural translation systems (e.g., Google NMT, Meta M2M-100) convert text while preserving context, idioms, and meaning.
- Voice Synthesis & Cloning – Tools like VMEG AI recreate the speaker’s original voice, maintaining tone, rhythm, and emotion in the target language.
- Lip-Sync & Timing – Some platforms align lip movements with dubbed audio; VMEG AI performs this during post-processing for natural results.
- Human Review & Quality Control – Editors check cultural nuance, terminology, and accuracy to ensure professional-quality output.
Applications of AI Localization
AI video localization is rapidly becoming an industry standard across multiple domains:
- Global Entertainment and Streaming
Localized content, for most of the streaming platforms, like Netflix and YouTube, is their money tree; they all depend on it to reach global audiences. Netflix's own research states that up to 70% of viewing hours outside of English-speaking nations consist of its localized programming.
AI translation can and will rock the film industry's world by letting amateur filmmakers and influencers duplicate its power.
- Education and E-Learning
The astounding thing is that in 2025, the e-learning industry still relies heavily on accessibility. Even though its value reached $460 billion globally.
The landscape has shifted. AI localization tools allow educators to instantly translate lectures, tutorials, and training videos for learners worldwide, promoting inclusion without prohibitive costs.
- Business Training and Corporate Communication
Multinational corporations use AI dubbing for internal communications, compliance videos, and HR training. This ensures consistency of message while saving localization budgets.
- Marketing and Advertising
Localized video ads convert far better than generic global ones. According to HubSpot 2024, regionally adapted videos improve engagement by 60%.
AI now enables marketers to adapt tone, humor, and even voice personalities to each market — all while keeping brand identity consistent.
- Accessibility and Inclusion
For the deaf and the hard-of-hearing, and those who speak minority languages, AI subtitles and dubbing make it easier for them to gain accessibility. According to a UNESCO report that localized educational content, in some way, improves retention and engagement for non-native English speakers by nearly 40%, really astounding.
Top AI Video Localization Tools and Platforms in 2025
The 2025 AI localization landscape is populated by a range of solutions, from research-grade systems to commercial applications. Each brings a different strength to the table.
|
Tool
|
Core Feature
|
Use Case
|
|
VMEG AI
|
Cross-language voice cloning with emotional preservation
|
Full multilingual dubbing for creators & enterprises
|
|
HeyGen
|
Avatar-based video + translation
|
Marketing videos, explainer content
|
|
ElevenLabs
|
Highly realistic AI voices
|
Podcasts, film dubbing
|
|
Descript (Overdub)
|
Voice cloning within video editing
|
Content creators & editors
|
|
Papercup
|
Enterprise-scale AI dubbing
|
Broadcaster & studio localization
|
|
Murf AI
|
Template-driven voiceovers
|
Marketing and corporate training
|
VMEG AI: A Leading Platform for AI Video Localization
VMEG AI is a cutting-edge video localization tool that demonstrates the progress of artificial intelligence.
AI dubbing that preserves tone and emotion, voice cloning across languages, and multilingual subtitle creation are all supported. You can select source and target languages, upload videos, and obtain fully localized outputs with dubbed audio or synced subtitles.
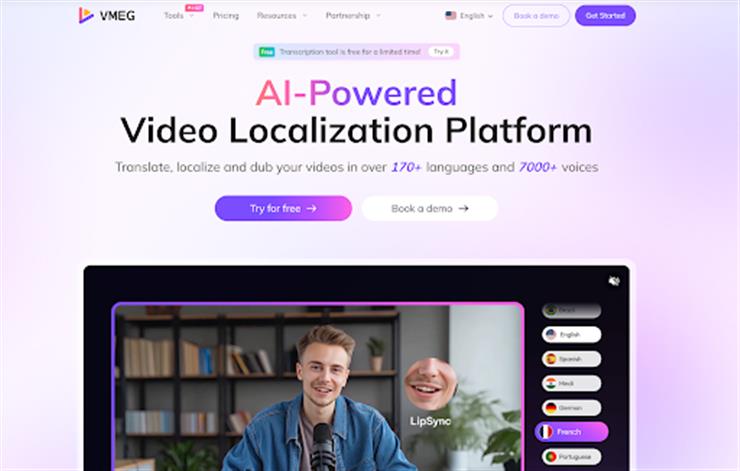
AI Video Localization Tool - VMEG AI
VMEG AI prioritizes authenticity—maintaining the speaker's vocal identity across languages—in contrast to many systems that merely translate text. For YouTubers, educators, and corporate communicators looking for worldwide consistency, this makes it very useful.
Key Features of VMEG AI:
- Multilingual Subtitle Generation: Automatic recognition and subtitle creation in 170+ languages.
- Subtitle Translation & Customization: Context-aware translation with adjustable font, size, style, and placement.
- Voice Cloning Across Languages: Preserves original tone, emotion, and vocal personality.
- Lip-Sync AI Video Creation: Synchronizes dubbed audio with on-screen lip movements.
- AI Script Generation: Automatically creates structured scripts from product info or content themes.
- Video & Audio Transcription: Near-perfect transcription accuracy in 170+ languages, with online editing tools.
- Multi-Speaker Detection: Identifies multiple speakers and assigns unique voices.
However, the platform remains online-only and not suitable for real-time translation — emphasizing quality over instant interaction.
The presence of tools like VMEG AI signals how localization has moved from an expensive studio process to an accessible creator technology.
Ethical and Quality Considerations
AI localization democratizes multilingual communication but raises ethical and quality concerns. Voice ownership is a key issue: cloned voices may require consent, and unions are already advocating for regulation (BBC News, 2024). This is lessened by platforms such as VMEG AI, which mandate that users provide their own content. Cultural bias is an additional problem that can arise when AI is trained on unequal datasets and misinterprets humor or idioms, leading to misalignment.
Data privacy is essential since voice and facial data are processed; capable platforms encrypt files and follow regulations like the EU AI Act. Notwithstanding these difficulties, there are definite advantages to AI translation, including lower expenses, greater accessibility, and assistance for authors in reaching a worldwide audience.
The Future of Global Communication
Revolutionary developments in AI localization are anticipated over the next ten years. Emotion, intent, and cultural context may soon be interpreted simultaneously by multimodal translation algorithms that comprehend gestures, tone, and images in addition to words.
Combined with avatars and holographic technology, this could enable “borderless communication, ” where a teacher in Seoul lectures in Portuguese to students in Brazil, or a journalist in Delhi broadcasts instantly in multiple languages. As one Quora respondent noted, “Localization isn’t about language anymore; it’s about presence. AI just makes that presence global.”
Conclusion
The story of AI video localization is not merely technological — it’s cultural. For decades, global communication has had its own pain spots, costs, logistics, and linguistic diversity.
Now, all driven by AI, with translation, voice cloning, and contextual understanding, creators, educators, and enterprises can connect with audiences anywhere, providing both authenticity and instantcy.
VMEG AI, ElevenLabs, and HeyGen, all high-ranking platforms, show us how localization no longer only belongs to studios, rather a creative tool for everyone.
It's to say that with any transformative technology, its progress must be well-balanced, with ethics, transparency, and respect for original voices all alright.
By 2030, it may no longer matter what language a video is made in — the story will simply find its audience. That is the true promise of AI localization: not replacing human expression, but amplifying it across the world’s many languages.